Defect of the Month
Back to AGR's Library
The white snowflakes floating across the background are actually dendritic zirconia (Zr2O3) crystals embedded in green glass, as viewed through a microscope. Zirconia dendrites are formed when run off from zirconia-containing refractories recrystallizes in the glass melt. Because the crystals do not preserve the original structure of the refractory, they are classified as a secondary type of stone defect. This pair of images is called a stereogram. When viewed properly, the combined image will appear three dimensional just as if you were looking through a stereomicroscope. To see the 3D image, follow these instructions: 1. Slowly move your face towards the image on your computer screen. 2. Allow the image from each eye to drift horizontally as your eyes lose focus. If you’re good at viewing “Magic Eye” type stereograms, this will come naturally. 3. Allow the images to drift far enough so that you see an out-of-focus frame on the left, a merged frame in the center, and an out-of-focus frame on the right. Your goal is to get an image of the left frame from one eye to merge with an image of the right frame from the other eye. Use the black borders to help you align the two images of the center frame so that they overlap. 4. You should now be observing a 3D effect on the merged image. If you cannot get the images to drift far enough, you may need to resize the stereogram so that it is smaller on your screen.
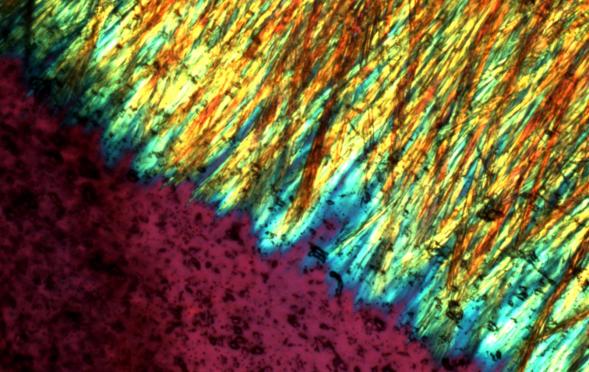
Devitrite crystals in soda-lime glass, viewed in a thin section under polarized light. Devitrite is a sodium and calcium silicate that forms radiating needle-like crystals. Stones of devitrite can crystallize from the glass melt in regions of the furnace that fall below the liquidus temperature.

The Molybdenum Streak (as viewed in polarized light) is either sodium or calcium molybdate due to high temperature lubricants near the forming machine, or the result of exposed molybdenum electrodes eroding into the glass. The latter may be due to either low glass level or electrical issues.

A seed is a gaseous bubble that gets trapped within the glass. This seedy column is a cluster of these bubbles.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 28
- Next page